THALASSEMIA

Thalassemia is a group of inherited blood disorders that affect the body's ability to produce hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. People with thalassemia produce either no or very low amounts of hemoglobin, which leads to anemia (a lack of healthy red blood cells). This can cause fatigue, weakness, and more severe complications if untreated. It is a challenging genetic blood disorder that requires continuous medical treatment, often including costly medicines. At Sky Organisation, we are committed to alleviating this burden by ensuring that patients have reliable access to the medications they need. Our goal is to bridge the gap between need and access, providing hope and support to families grappling with the effects of this condition.
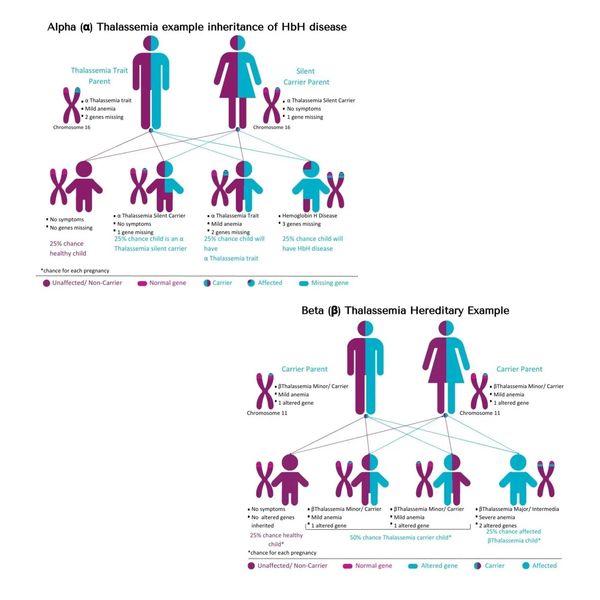
Types of Thalassemia
1. Alpha Thalassemia: Occurs when one or more of the four alpha globin genes (responsible for making hemoglobin) are missing or mutated.
- Alpha Thalassemia Trait: When one or two genes are affected. Symptoms are mild or absent.
- Hemoglobin H Disease: When three genes are affected. Leads to moderate to severe anemia.
- Alpha Thalassemia Major (Hydrops Fetalis): All four genes are affected, usually causing stillbirth or death shortly after birth.
2. Beta Thalassemia: Caused by mutations in the beta globin genes.
- Beta Thalassemia Minor (Trait): One mutated gene. Causes mild anemia.
- Beta Thalassemia Intermedia: Two mutated genes, leading to moderate anemia.
- Beta Thalassemia Major (Cooley's Anemia): Two severely mutated genes, resulting in severe anemia that requires regular blood transfusions.
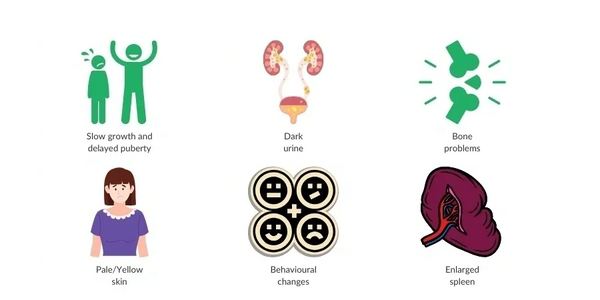
Symptoms
- Mild Thalassemia: May show little to no symptoms.
- Moderate to Severe Thalassemia: Can cause-
- Severe anemia
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin (jaundice)
- Bone deformities, especially in the face
- Delayed growth
- Enlarged spleen
- Heart problems

Causes
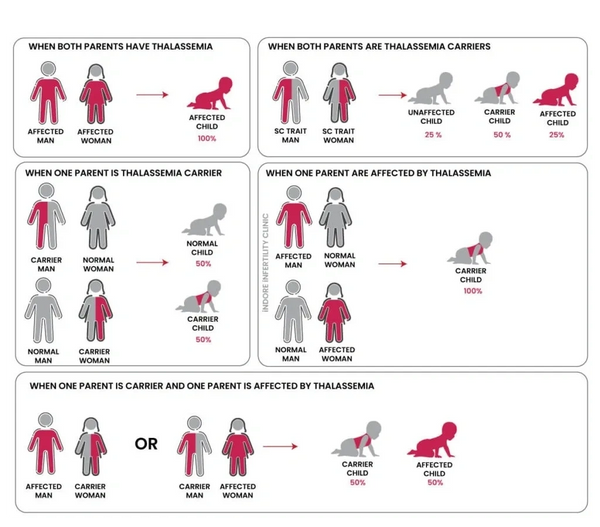
- Inherited Genetic Mutations: Thalassemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the mutated gene to pass the disorder to their offspring. If only one parent passes the gene, the child may have a milder form (thalassemia minor or trait).
- Geographic Prevalence: Thalassemia is more common in individuals of Mediterranean, African, Middle Eastern, and Southeast Asian descent. This higher prevalence is thought to be related to the protective effects of carrying one thalassemia gene against malaria in these regions.
In summary, thalassemia is caused by mutations in the genes responsible for hemoglobin production, inherited from both parents, and affects the ability of red blood cells to function properly.
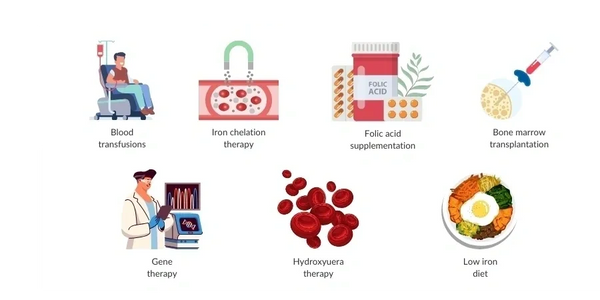
Treatment
The treatment for thalassemia depends on its severity:
- Mild Cases: May require little or no treatment.
- Severe Cases: Often require regular blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy (to remove excess iron from the blood), and in some cases, a bone marrow or stem cell transplant.
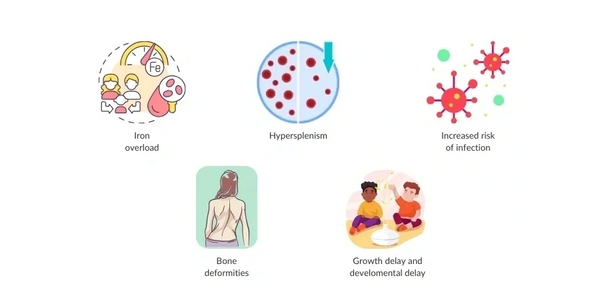
Complications
Without proper treatment, thalassemia can lead to:
- Iron overload from blood transfusions, which can damage the heart, liver and other organs.
- Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)
- Growth problems
- Heart or liver failure
Impact of Thalassemia
Global Impact
- Carriers: About 1.5%–7% of the global population (roughly 90 million to 350 million people) are carriers of a thalassemia gene (alpha or beta thalassemia).
- Thalassemia Patients: It is estimated that around 300,000 to 400,000 babies are born with severe forms of thalassemia (like beta-thalassemia major) every year.
- Thalassemia is most common in regions such as:
- Mediterranean countries (e.g., Greece, Italy)
- The Middle East
- South Asia (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh)
- Southeast Asia
- Parts of Africa
India-Specific Impact
- Carriers: India is a major hotspot for thalassemia. Around 3%–4% of the Indian population (roughly 35–45 million people) are estimated to be carriers of the thalassemia trait (also known as beta-thalassemia minor).
- Thalassemia Patients: India sees around 10,000–12,000 children born each year with thalassemia major. Currently, it is estimated that over 100,000 people in India live with thalassemia major.
- The high prevalence in India is partially due to consanguineous marriages (marriages between close relatives) in some communities, which increases the likelihood of inheriting the disease from both parents.
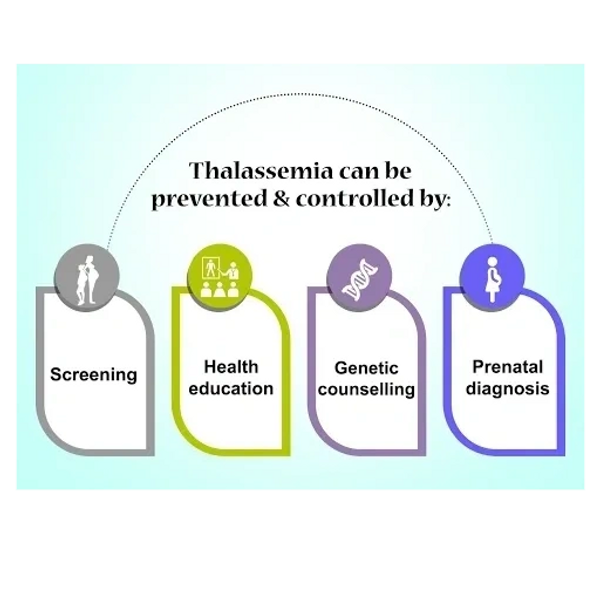
Prevention and Management
Genetic counselling is important for individuals with a family history of thalassemia, especially for those considering having children. In some cases, prenatal testing can detect thalassemia in the developing fetus. Advances in gene therapy hold potential for future treatments.